
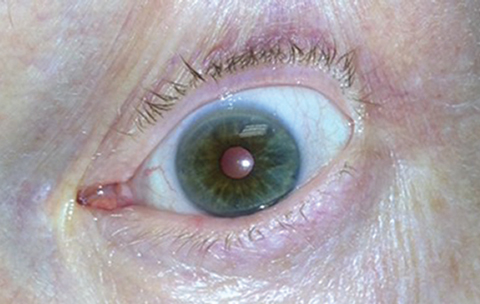
IP assessments from follow-up appointments ( A, B, time 4-15 months) indicate some return of pupillary symmetry between both pupils and nominal increases in NPi values for the right pupil by month four. Initial IP NPi scores ( A, time 0 months) and IP size measurements ( B, time 0 months) show some asymmetry between the pupils and no pupillary function on the right side. Initial CT studies (C, D) revealed a left-sided basal ganglia hemorrhage. Patient three is a 12-year-old helmeted male motorcross cyclist involved in a crash. No return of pupillary function: relationship of NPi scores, pupillary asymmetry, and brain images. Infrared pupillometry Neurological Pupil index Oculomotor nerve palsy Pupillary outcome Pupillometer Traumatic brain injury Traumatic third nerve palsy. We found that NPi scores, as a component of the clinical exam, provide a sensitive, noninvasive and quantitative means of following pupillary function acutely and chronically after a traumatic brain injury. Early NPi score normalization suggests pupillary function may improve. A unilateral blown pupil and abnormal NPi score in a traumatic brain injury patient are not necessarily indicative of intracranial pressure issues, and must be correlated with the entire clinical scenario, to determine the etiology of the third nerve injury and direct potential therapeutic interventions. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography imaging studies, with a focus on the third nerve, revealed focal abnormalities consistent with the clinical findings. Anisocoria improved in all patients despite concurrent abnormal NPi scores. Two patients showed early improvement in NPi scores correlating with the normalization of their pupillary reactivity. One patient with consistent abnormal NPi scores and an improved clinical exam did not undergo invasive interventions. Two patients underwent subsequent intracranial pressure monitoring based on a deteriorating clinical scenario, including consistent abnormal unilateral NPi scores. Each patient was monitored closely in the trauma bay for neurological deterioration with a pupillometer and the clinical exam. Five traumatic brain injury patients were identified with unilateral pupillary dysfunction with long-term follow-up after the initial injury.
Clinical exam findings of pupillary size, NPi scores, and brain Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Computed Tomography images were analyzed. A retrospective chart review was performed of traumatic brain injury patients with acute unilateral pupillary dilation, admitted to Legacy Emanuel Medical Center's NeuroTrauma Unit, Portland, OR, and followed as outpatients, between January 2012 and December 2013. NPi technology applies a scalar value to pupillary function. Patients were monitored closely with an infrared pupillometer, with NPi technology, for acute changes in pupillary function. Pupillary dysfunction, a concerning finding in the neurologic examination of the patient with an acute traumatic brain injury often dictates the subsequent treatment paradigm.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
